The GitHub Copilot SDK marks a paradigm shift in how modern apps are built and developed, moving away from static prompts toward an agent-based execution loop at the foundation of application logic. This new paradigm enables developers to embed the same production-tested runtime used by Copilot CLI directly into their own applications, unlocking multi-step planning, multi-model orchestration, tool execution, streaming responses, authentication, and Model Context Protocol (MCP) integration.
As AI-native software becomes more sophisticated, this new approach will redefine how developers build intelligent systems that think, react, and adjust in real time.
What Is the GitHub Copilot SDK?
The GitHub Copilot SDK is a developer framework that reveals the Copilot CLI runtime to use in custom applications. Instead of defining AI as an API that responds to a single request, it is an SDK that lets you run stateful and long-running AI agents that schedule tasks, use tools, analyse results, and repeat until the goals are achieved.
This SDK was intended for use in production environments with a focus on reliability, extensibility and security, which are essential specifications for enterprise-class AI applications.
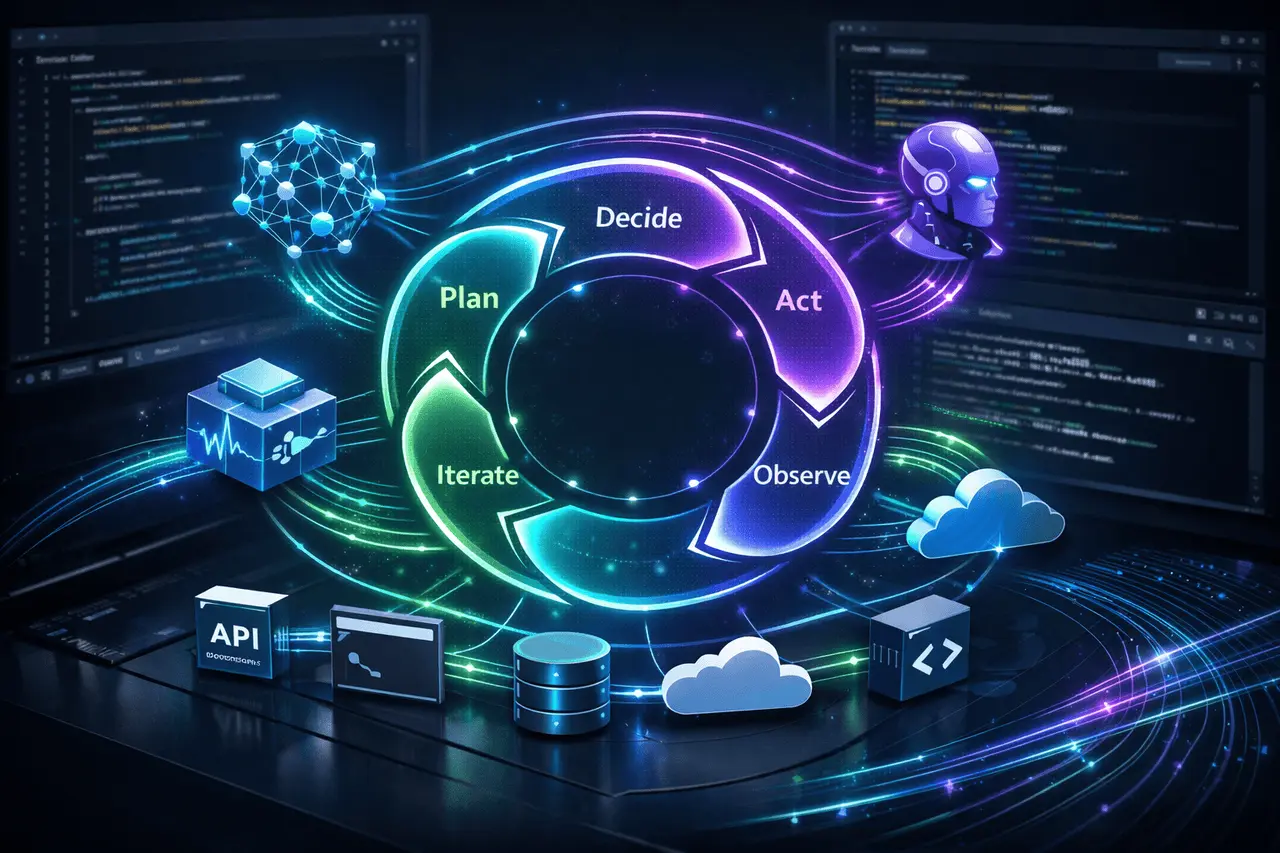
Understanding the Agentic Execution Loop
What “Agentic” Means in Practice?
A loop of execution by agents is a continuous loop wherein it is the case that an AI computer:
- Interprets the goal
- Steps to get there are as follows:
- Executes actions by using APIs or tools
- Observes results
- Modifies the plan and repeats the process as required
In contrast to conventional request-response AI workflows, agents maintain context across stages and make autonomous decisions within specific constraints.
Why the Execution Loop Matters?
This loop lets applications manage complex, multi-step processes like troubleshooting codebases, orchestrating cloud resources, or automating business workflows without coding every decision path.
Core Capabilities Exposed by the SDK
Multi-Model Orchestration
The SDK supports multi-model execution, enabling applications to send tasks to different models based on capabilities, costs, or latency requirements. This allows:
- Specialised models for planning vs execution
- Strategies for fallback to ensure reliability
- Optimised performance across workloads
Multi-Step Planning and Reasoning
Instead of producing an output in one go, the agents can break tasks into stages, complete the steps sequentially, and modify plans based on intermediate outcomes.
Tool Invocation and Action Execution
Agents can make calls to external tools, like scripts, APIs, and system commands, to perform first-class actions. This enables AI systems to shift beyond “advice” to”action..
Streaming Responses
The SDK can stream outputs, enabling real-time feedback for interactive apps such as dashboards, developer tools, and chat interfaces.
Authentication and Secure Context Handling
Built-in authentication methods ensure agents have the correct permissions, making the SDK ideal for enterprise and internal tools.
MCP Integration
The Model Context Protocol (MCP) integration standardises how agents access shared context, tools, and resources across environments, reducing fragmentation and improving interoperability.
From Traditional AI Apps to Agentic Apps
Traditional vs Agentic Application Design
| Aspect | Traditional AI Apps | Agentic Apps with Copilot SDK |
|---|---|---|
| Interaction Model | Single prompt → response | Continuous execution loop |
| Context Handling | Stateless | Stateful and persistent |
| Tool Use | Manual integration | Native, autonomous tool calls |
| Planning | Hardcoded logic | Model-driven planning |
| Adaptability | Limited | Dynamic and self-correcting |
This fundamental shift changes how developers think about application flow and their responsibilities.
Real-World Use Cases
Developer Tooling
Agentic workflows can be used to support code analysis and refactoring, as well as dependency updates and repository-wide reasoning, mirroring and extending the capabilities of Copilot CLI within customised tools.
DevOps and Infrastructure Automation
Agents can design deployment steps, implement infrastructure changes, check results, and roll back when needed — all in a monitored loop.
Enterprise Knowledge Systems
AI agents can retrieve documents, ask the internal system, organise results, and refine answers to complex business queries.
Productized AI Features
embedding agentic runtimes into applications enables intelligent assistance, automated workflows, and a more flexible user experience.
Benefits of the Agentic SDK Approach
Key Advantages
- Runtime that has been Tested in Production: Same Core used for Copilot CLI.
- Reducing Glue Codes: Planning and orchestration of the tool is managed by an agent
- Intelligence that Scales: Multi-model and multi-step design
- More UX-friendly: streaming and feedback loops that iterate
- A Future-Friendly Architecture: created to adapt to the changing AI capabilities
These advantages make the SDK especially appealing to teams building AI-first, long-lived platforms
Limitations and Practical Considerations
Increased Complexity
Agentic systems introduce new challenges in debugging, observability, and testing. Developers need to design security measures and monitor them carefully.
Cost and Resource Management
Multiple-step execution, as well as tool use, can increase the cost of computation and API when not properly constrained.
Determinism and Control
While autonomy is extremely powerful, specific applications need strict control. The balance between flexibility and control is crucial.
How does this change the Developer Workflow?
The GitHub Copilot SDK allows for an entirely new workflow in which developers can:
- Goals are defined instead of rigid flows
- Offer tools instead of a fixed logic
- The guidelines for behaviour based on the constraints and policies
- Let agents handle execution details
This is similar to how humans develop software: planning, executing, measuring results, and iterating to bring software to the concept of collaborative intelligence.
My Final Thoughts
The Copilot SDK by GitHub provides agents in the execution loop, which is an application-specific first-class primitive which signals a larger change in the design of software. Incorporating a production-grade multi-model, tool-aware runtime into their apps, developers can build systems that plan, react, and adapt with greater autonomy.
While AI continues to transform from passive agents into active partners, agents like this could be the foundation for an era of artificial intelligence, changing the way applications are developed, operated, and used.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What’s an agentic execution loop used in AI applications?
The agentic execution loop (AEL) is an ongoing sequence that occurs when an AI plans, executes actions, assesses the results, and repeats until a target is met.
2. How is the GitHub Copilot SDK different from calling an AI API?
The SDK provides a complete runtime for multi-step agents that use tools beyond one-time responses to prompts.
3. Is the SDK used with different AI models?
Yes. It supports multi-model orchestration, enabling different models to be used for planning, reasoning, and execution.
4. What function does MCP contribute to the SDK?
MCP defines how agents interact with everyday contexts, applications, and resources, ensuring consistency across different environments.
5. Does this approach work for applications that are used in the enterprise?
Yes. Integrated authentication, streaming and production-tested components make it ideal for both internal and corporate tools.
6. How is the GitHub Copilot SDK different from calling an AI API?
No. They can complement it by handling complex, adaptive tasks, while the fundamental business rules are clearly specified.
Also Read –
Microsoft Copilot Checkout: In-App Payments with Stripe & PayPal