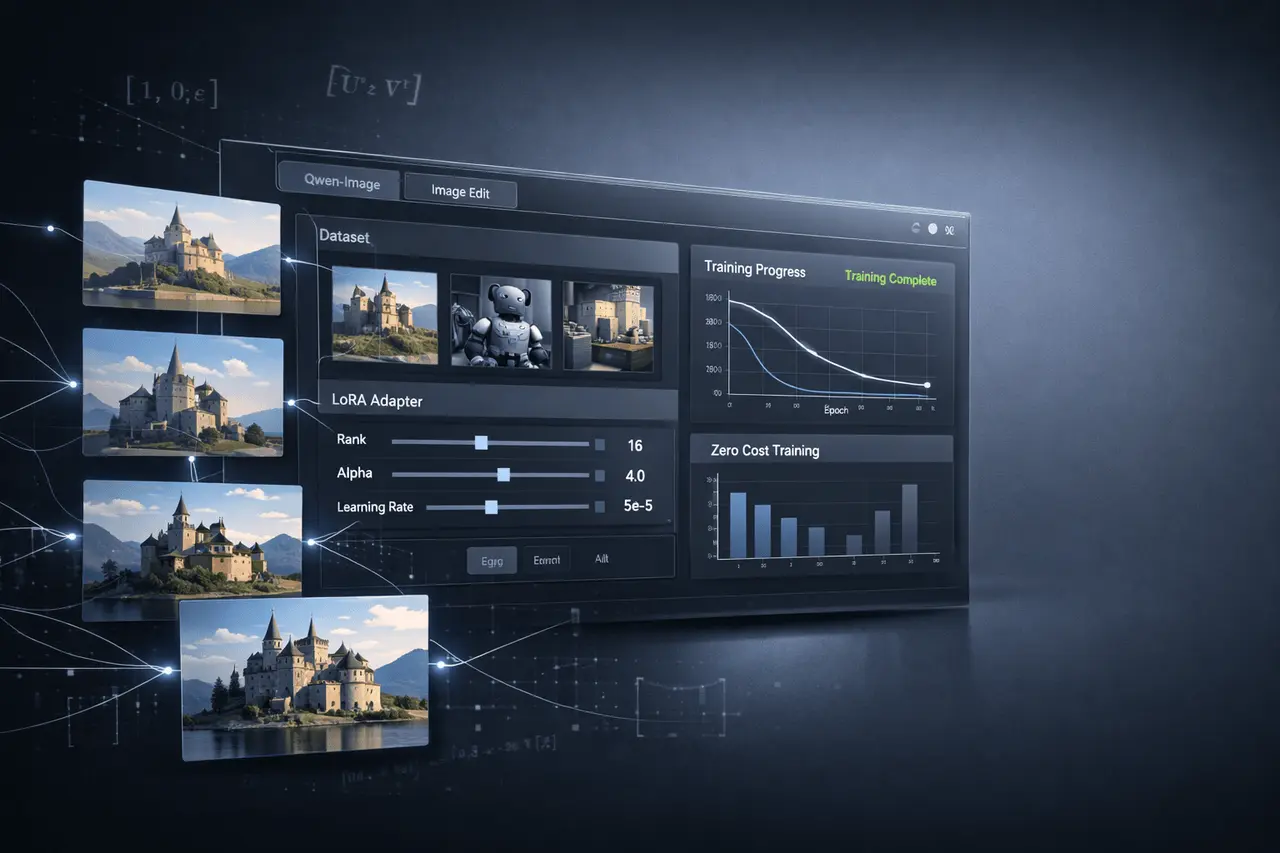
The pace of progress in image generation has been rapid, but customisation has often remained expensive or technically demanding. That balance is shifting. Model builders and creators can now fine-tune advanced image models using Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) without upfront training costs, directly on ModelScope. This update makes professional-grade image customisation more accessible to developers, researchers, and independent creators alike.
At launch, free LoRA training is available for three high-capability image models: Qwen-Image-2512, Z-Image-Turbo, and Qwen-Image-Edit-2511. Each targets a different part of the image generation workflow, from high-fidelity synthesis to rapid iteration and precise editing. Together, they mark a meaningful expansion of what can be built quickly and affordably on a shared AI platform.
Why LoRA Matters for Image Models?
LoRA has become one of the most practical techniques for adapting large models to specific styles or tasks. Instead of retraining an entire network, which is costly in compute, time, and expertise, LoRA introduces a small set of trainable parameters layered on top of an existing model.
For image generation, this approach has several advantages:
- Lower Compute Requirements: Only a fraction of parameters are updated.
- Faster Training Cycles: Fine-tuning can be completed in hours rather than days.
- Model Integrity: The original base model remains unchanged.
- Easy Portability: LoRA weights can be reused, shared, or swapped without distributing full models.
By offering LoRA training at no cost, ModelScope removes one of the most common bottlenecks faced by smaller teams: experimentation constrained by GPU budgets.
What’s New on ModelScope?
The update introduces free LoRA training workflows directly within the platform. Users can upload datasets, configure training parameters, and generate LoRA adapters without leaving the ecosystem or setting up local infrastructure.
Key aspects of the release include:
- Zero-cost entry point: No training fees for supported models.
- Integrated tooling: Dataset handling, training, and evaluation in one place.
- Production-ready outputs: LoRA adapters that can be deployed or shared.
- Support for multiple image tasks: Generation, fast inference, and image editing.
This combination targets both experimentation and real-world use, not just demos.
The Supported Models and Their Roles
Qwen-Image-2512: High-Quality Image Generation
Qwen-Image-2512 is designed for detailed, high-resolution image synthesis. It emphasises composition accuracy, texture fidelity, and prompt alignment. With LoRA fine-tuning, creators can adapt the model to:
- Specific visual styles or aesthetics
- Brand-consistent imagery
- Domain-focused datasets, such as product images or illustrations
This makes it particularly useful for design teams, content creators, and researchers working on visual specialisation.
Z-Image-Turbo: Speed-Focused Iteration
Z-Image-Turbo prioritises fast inference and responsiveness. While it may trade some depth for speed, its performance profile is ideal for rapid prototyping, previews, and interactive applications.
LoRA training on this model enables:
- Quick experimentation with new styles
- Lightweight customisation for real-time tools
- Efficient deployment where latency matters
For startups or teams building user-facing applications, this balance between speed and customisation is critical.
Qwen-Image-Edit-2511: Precision Image Editing
Unlike pure generation models, Qwen-Image-Edit-2511 focuses on controlled image transformation. Tasks include object replacement, style transfer, and localised edits guided by text or reference images.
Fine-tuning with LoRA allows the model to learn:
- Consistent editing behaviours
- Domain-specific transformations
- Improved alignment with specialised datasets
This opens up use cases in photo editing, creative workflows, and automated design adjustments.
Lowering the Barrier to Custom Image AI
Historically, fine-tuning image models required a mix of cloud credits, ML engineering skills, and infrastructure management. By bundling free LoRA training into a managed platform, ModelScope simplifies that process.
This shift benefits several groups:
- Independent developers can test ideas without financial risk.
- Researchers can validate hypotheses quickly.
- Small businesses can build branded image systems without large budgets.
- Educators and learners gain hands-on experience with modern AI workflows.
The result is a more level playing field, where innovation depends more on ideas than resources.
How This Fits into the Broader AI Ecosystem?
The models supported in this rollout are part of the broader Qwen family, developed within Alibaba Cloud’s Ecosystem. Their availability on ModelScope reflects a growing trend: pairing open or semi-open foundation models with accessible customisation tools.
Rather than distributing massive checkpoints or forcing users into self-managed pipelines, platforms are increasingly focusing on:
- Hosted training experiences
- Modular fine-tuning methods like LoRA
- Clear paths from experimentation to deployment
This approach accelerates adoption while maintaining technical rigour.
Practical Considerations Before You Start
While the training itself is free, effective results still depend on preparation. Users should consider:
- Dataset Quality: Clean, well-labelled images matter more than sheer volume.
- Scope of Customisation: LoRA excels at style and behaviour adaptation, not full retraining.
- Evaluation Workflows: Testing outputs across varied prompts is essential.
Free access lowers the cost of mistakes, but thoughtful setup still determines success.
What does this enable going forward?
The significance of this update lies less in the announcement itself and more in what it unlocks. Free LoRA training on capable image models encourages:
- Faster iteration cycles
- More niche and creative applications
- Community-driven experimentation and sharing
As more users fine-tune and deploy adapters, the ecosystem around these models is likely to grow more prosperous and more diverse.
My Final Thoughts
Free LoRA training on ModelScope is less about a single feature release and more about a shift in access. By removing cost and infrastructure friction, it encourages experimentation, niche creativity, and faster iteration across image generation and editing workflows. When customisation becomes easy to start, better ideas surface sooner. For teams and individuals building with image AI, this update turns fine-tuning from a long-term plan into an immediate next step.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is LoRA training on ModelScope really free?
Yes. LoRA training for supported image models is available at no cost, reducing the cost of experimentation and customisation.
2. Do I need my own GPUs to fine-tune these models?
No. Training runs within the ModelScope platform, so you don’t need to manage local or cloud GPU infrastructure.
3. What kind of datasets work best for image LoRA training?
Curated, domain-specific datasets with consistent visual patterns typically produce the best results, even when modest in size.
4. Can LoRA adapters be reused across projects?
Yes. LoRA adapters are lightweight and can be applied, swapped, or shared across compatible workflows without retraining the base model.
5. Is this suitable for production use?
The generated LoRA adapters are production-ready, but teams should still validate outputs, performance, and licensing alignment before deployment.
6. How does this differ from full model fine-tuning?
LoRA modifies a small subset of parameters, making training faster and cheaper while preserving the original model’s capabilities.
Also Read –
Qwen Code v0.6.0: New Skills, Providers and CLI Updates
Qwen-Image-2512: Strongest Open-Source AI Image Model